With the rapid deployment of Wi-Fi 7 technology, Qualcomm’s QCN9274 and QCN6274 have become core chipsets in next-generation wireless modules due to their high performance, multi-band support, and advanced MIMO capabilities. A critical design decision is the choice of interface format. This article provides an in-depth comparison of M.2 SLOT (2×2 5G & 2×2 6G) versus mini PCIe SLOT (2×2 5G & 2×2 6G) for these modules, offering valuable insights for hardware developers and system integrators.
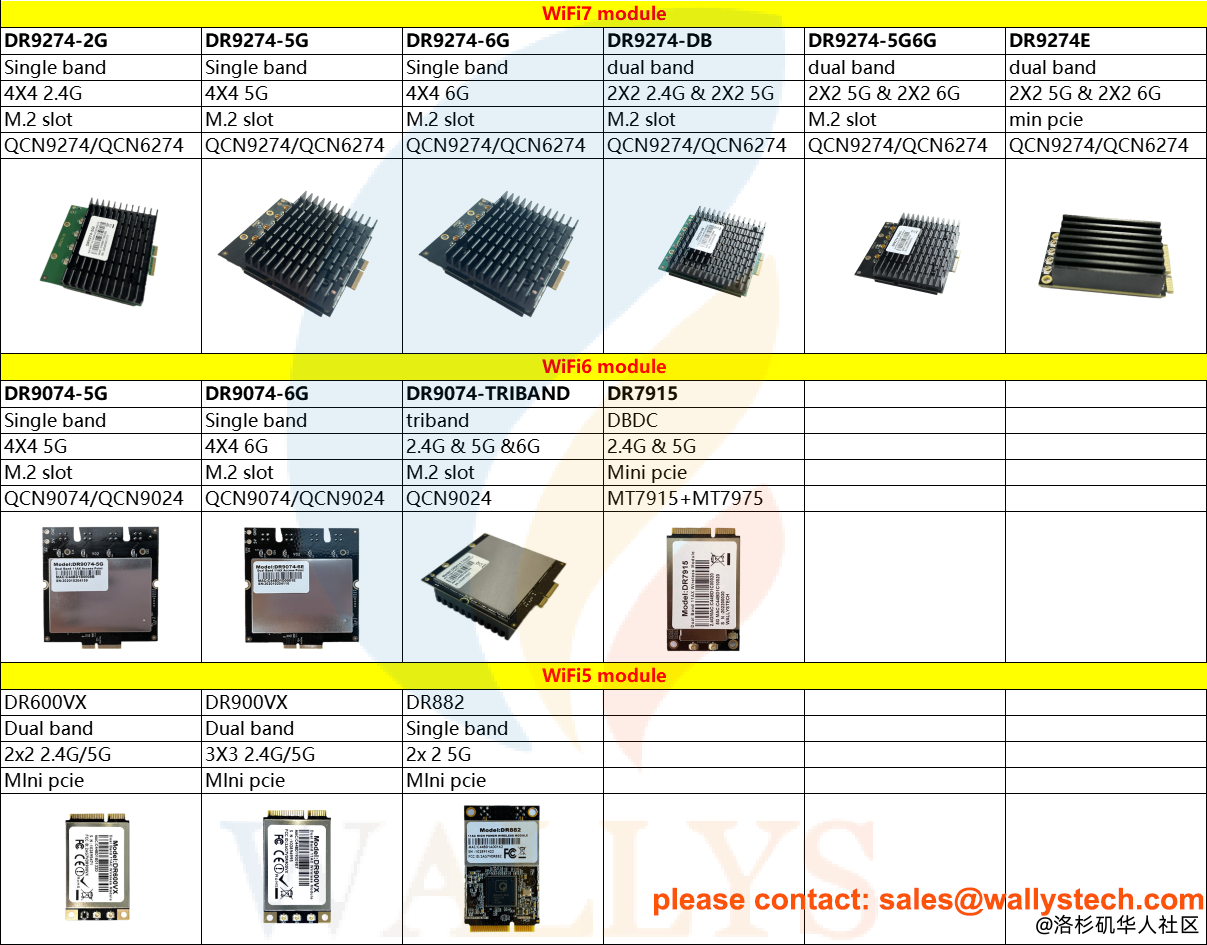
1. Background: QCN9274 / QCN6274 Overview
Process Technology: 7nm for low power and high integration
Frequency Support: 2.4GHz / 5GHz / 6GHz (Tri-band capable)
MIMO Capability: Up to 4×4 (typically configured as 2×2)
Interface: PCIe 3.0
Applications: Enterprise routers, industrial IoT, CPE, gateways, APs, edge computing, etc.
2. Interface Comparison: M.2 vs mini PCIe
| Feature | M.2 (Key A/E) | mini PCIe |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | PCIe 3.0 x1 or x2 (up to 8GT/s) | PCIe 2.0 x1 (up to 5GT/s) |
| Form Factor | Smaller (e.g., 2230/3042/3052) | Larger (30×50.95mm standard) |
| Power Management | More efficient, finer control | Less optimized |
| Market Trend | Preferred for new Wi-Fi 6/6E/7 designs | Legacy support, phasing out |
3. Technical Considerations for QCN9274/QCN6274
1. Bandwidth and Throughput
Wi-Fi 7 supports up to 320MHz channel width and 4096-QAM, requiring very high throughput.
With 2×2 5G + 2×2 6G configuration, total wireless throughput can exceed 5Gbps.
M.2 (PCIe 3.0) offers better bandwidth headroom and performance stability compared to mini PCIe.
2. Physical Design and Thermal Management
M.2 offers flexible size options (e.g., 3052), ideal for slim devices and compact edge gateways.
mini PCIe's larger footprint can be limiting in space-constrained designs.
M.2 modules can support dedicated heatsinks or backside cooling for better thermal handling, especially for high-frequency 6GHz operation.
3. Compatibility and Expandability
mini PCIe is still common in legacy systems (older industrial PCs, x86 boards).
M.2 is the standard in modern embedded and consumer platforms.
M.2 is more future-proof and expandable, aligning with next-gen hardware.
4. Application Scenario Recommendations
| Use Case | Recommended Interface | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| New Wi-Fi 7 APs, Mesh systems | M.2 | Higher throughput, better thermal design |
| Edge computing and industrial IoT | M.2 or mini PCIe | M.2 if supported by host board |
| Legacy embedded systems | mini PCIe | Ensures backward compatibility |
| Enterprise-grade CPE / SMB Routers | M.2 | Compact layout and power efficiency |
| ODM/OEM Wi-Fi 7 product development | M.2 | Design flexibility and scalability |
5. Market Trend and Strategic Advice
Strong shift towards M.2: Most next-gen Wi-Fi 6E/7 modules (e.g., Intel BE200, Qualcomm reference designs) are adopting M.2 interfaces.
mini PCIe is fading: Although still in use, it’s no longer favored in modern designs.
Conclusion:
For developing Wi-Fi 7 modules based on QCN9274/QCN6274, M.2 SLOT (3052 format) with 2×2 5G + 2×2 6G configuration is highly recommended. This option ensures superior performance, scalability, thermal efficiency, and long-term compatibility—making it ideal for future-proof commercial and industrial-grade Wi-Fi 7 solutions.
6. Additional Design Tips
Use IPEX MHF4 connectors for antenna flexibility
Include active cooling or thermal pads to manage high-frequency heat
Implement RF shielding between 5G and 6G bands
Ensure firmware/software support for OpenWRT, QSDK, or OpenWiFi to simplify integration
Comments
Post a Comment